A traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track the route packets take from a computer to a destination, such as a website. It can be used to diagnose problems with a network or to find out where bottlenecks are occurring. To run a traceroute, the user enters the command “tracert” followed by the destination’s URL or IP address. The tool then displays a list of the intermediate devices between the computer and the destination, along with the time it takes for packets to travel to each device.
If you want to know What is a traceroute? how do you run it? you’ve come to the right place! Here at our blog, we aim to provide you with all the information you need to know about this popular networking tool.
traceroute is a diagnostics tool that helps you troubleshoot network issues by tracing the route that data takes from your computer to its destination. By understanding how data travels, you can better identify where problems may lie. So sit back, grab a cup of coffee (or tea, if that’s your preference), and get ready to learn all there is to know about traceroute!
What is a traceroute?
A traceroute is a tool that lets you see the path that data takes from your computer to a destination server. By running a traceroute, you can see how many “hops” your data makes and how long each hop takes.
This can be helpful in diagnosing network problems or simply in understanding how data travels across the internet. To run a traceroute, you’ll need to use the Command Prompt (Windows) or Terminal (Mac). From there, you’ll type in the command “tracert” followed by the destination server’s address.
For example, to run a traceroute to Google, you would type “tracert google.com“
” Once you hit enter, the traceroute will begin and you’ll see the results on screen.
How do you run a traceroute?
A traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to trace the path of packets from a source computer to a destination computer. It can be used to determine the route taken by packets across an IP network and to measure transit delays of packets on the network.
To run a traceroute, you will need to use the Command Prompt in Windows or the Terminal in macOS. In the Command Prompt or Terminal, you will need to type in the following command:tracert [destination]Replace [destination] with the IP address or hostname of the computer you are trying to reach. For example, if you are trying to run a traceroute to Google, you would type in the following command:tracert google.com
Once you have typed in the command, press Enter and the traceroute will begin. It will show you the route taken by the packets and the transit delays of each hop.
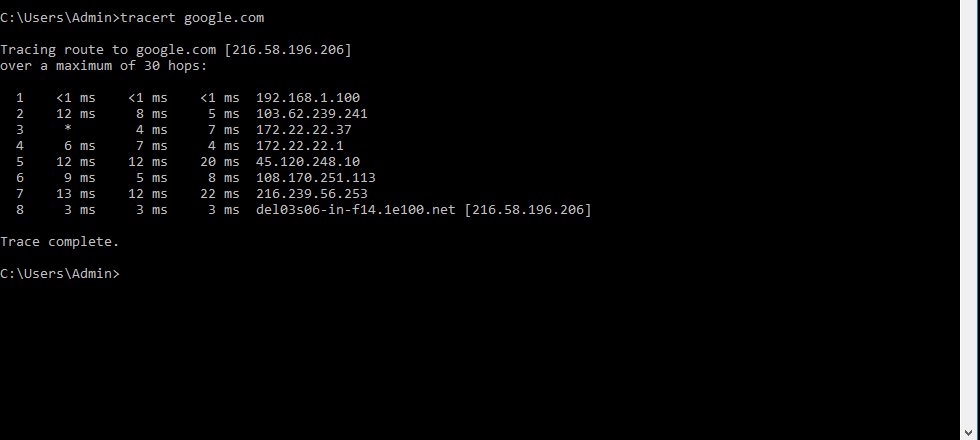
What do the results of a traceroute mean?
When you run a traceroute, you’re essentially sending a “ping” to a destination server to see how long it takes to get a response. A traceroute can be used to determine the amount of time it takes for a packet of data to travel from your computer to the destination server.
This can be useful for diagnosing slow internet connections or for troubleshooting network problems. To run a traceroute, you’ll need to use the Command Prompt (for Windows users) or the Terminal (for Mac and Linux users). From there, you’ll just need to type in the command “tracert” followed by the destination URL or IP address.
After a few seconds, you should see a list of the servers that your data is passing through on its way to the destination. The results of a traceroute can be a bit confusing, but essentially each line represents a “hop” from one server to the next. The first column represents the number of the hop, the second column represents the amount of time it took for the data to reach that server, and the third column represents the IP address or URL of the server.
If you’re troubleshooting a slow internet connection, you can use the traceroute results to see where the bottleneck is. If you see that the majority of the time is being spent on one particular hop, then that’s likely the server that’s causing the problem.
You can then contact your ISP or the server’s administrator to resolve the issue.
How can a traceroute be used to diagnose network problems?
A traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track the path of packets from a source computer to a destination computer. It can be used to diagnose network problems and determine why a connection is slow or failing.
To run a traceroute, you will need to open a command prompt and type the following command: tracert [destination].
This will return a list of the hops between your computer and the destination, as well as the time it takes for each hop. If you see a high number of hops or a long delay between hops, this could indicate a problem with the network.
Traceroutes can be used to diagnose network problems and determine where the bottleneck is.
Using a traceroute to diagnose a real-world network problem.

When you’re troubleshooting a network issue, one of the first tools you should reach for is a traceroute. A traceroute is a utility that shows you the path that your data takes from your computer to its destination.
It’s a helpful tool for diagnosing network problems because it can show you where along the route the problem is occurring. To run a traceroute, you’ll need to open a command prompt (on Windows) or a terminal window (on macOS and Linux). From there, you can type the command “tracert” followed by the address of the website or server you’re trying to reach.
The traceroute will then display the path that your data takes, along with information about each hop along the way. If you’re having trouble reaching a particular website or server, a traceroute can be a helpful tool for diagnosing the problem. It can show you where along the route the issue is occurring, and that can give you a clue as to what the problem might be.
Troubleshooting tips for common traceroute problems.
A traceroute is a diagnostic tool used to track the path of a packet across an IP network. The traceroute command is available on most operating systems, and allows you to view the route that a packet takes from your computer to its destination.
Traceroute can be useful for troubleshooting network problems, or for simply understanding how data travels across the Internet. In this article, we’ll show you how to use the traceroute command, and offer some troubleshooting tips for common traceroute problems. To run a traceroute, simply open a terminal or command prompt and type traceroute followed by the destination address.
For example, to trace the route to Google’s servers, you would type:traceroute www. google. comThis will show you the route that your data takes to reach Google, along with the time it takes for each hop.
By default, traceroute will use the ICMP protocol to send data, but you can also specify UDP or TCP with the -P option. For example, to use UDP:traceroute -P udp www.google. com
If you’re having trouble reaching a specific website or server, running a traceroute can help you to identify the problem. If you see that the packet is being routed through a particularly slow or congested hop, you may be able to improve your connection by avoiding that route. Another common use for traceroute is to determine the location of a server.
By looking at the IP addresses of the hops, you can often get a general idea of where the server is located. If you’re having trouble running a traceroute, there are a few things you can try. First, make sure that you have administrator privileges, as traceroute requires these to run. If you’re still having trouble, try using a different protocol. As we mentioned above, the ICMP protocol is the default, but you can also use UDP or TCP.
If one protocol isn’t working, another may be able to get through. Finally, if you’re still having trouble, it’s possible that your firewall is blocking the traceroute. Try disable your firewall temporarily to see if this is the case. Hopefully, this article has helped you to understand how traceroute works, and how you can use it to troubleshoot network problems.
FAQs about traceroutes
A traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to determine the route taken by packets across an IP network. It employs the IP protocol’s time to live (TTL) field and attempts to elicit an ICMP TIME_EXCEEDED response from each node in the path to the destination.
The traceroute command is available on most Unix-like operating systems. Windows users can use the tracert command. The utility can be very useful for troubleshooting network connectivity issues.
To run a traceroute, simply type the command followed by the destination hostname or IP address. For example, the following command would trace the route to google.
traceroute google.com
The output of the command will show the route taken by the packets and the time taken to reach each node.
Conclusion
A traceroute is a network diagnostic tool used to track the path of packets from a source computer to a destination computer. A traceroute can be used to diagnose network problems or to determine the location of bottlenecks.
To run a traceroute, a user must enter the command “traceroute” followed by the destination IP address or hostname.


